While land-based earthworks projects typically have contoured design levels, coastal projects tend to be somewhat simpler, involving a series of flat areas to be dredged or reclaimed. For this reason, some design elements available in Kubla Cubed are rarely used on coastal projects. The following two elements are typically the most useful:
-
Platforms: Used to define flat areas by drawing the outline of the flat area. These are useful for dredging berth pockets and turning circles, for example.
-
Paths: Used to define areas by drawing a centreline and specifying the width. These are useful for dredging channels, for example.
Cut Only and Fill Only
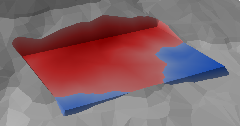
One of the key differences between typical coastal engineering projects and land-based earthworks is that only cut or only fill is often specified. For example, in a dredging project, you only remove material and do not fill to the designed level. Since Kubla Cubed has been used for coastal engineering from the outset, this has always been an option on every earthworks element. Achieving this is simply a matter of setting the ‘Mode’ to ‘Cut’ instead of the default ‘Cut & Fill’.
 |

|
| Mode: Cut & Fill | Mode: Cut |
The cut-only mode, which is rarely used on land-based projects, is routinely required for coastal projects.
Side Batters
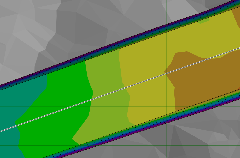
One powerful feature of Kubla Cubed is the ability to automatically generate side batters to slope between the design ground levels and the existing bathymetry. This is particularly important for coastal projects, where the batter angles can be quite low, and the volumes within these batters can represent a significant part of the total volumes. See Side Batters.
 |
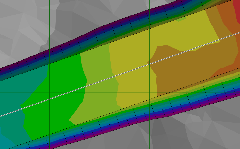 |
| Side Batters: Off | Side Batters: External |
Side batters can comprise a significant part of the volumes on coastal projects. Kubla Cubed generates them automatically and you can adjust the batter angles as required.